Building a Secure Kubernetes Cluster with Fortigate & Hyper-V
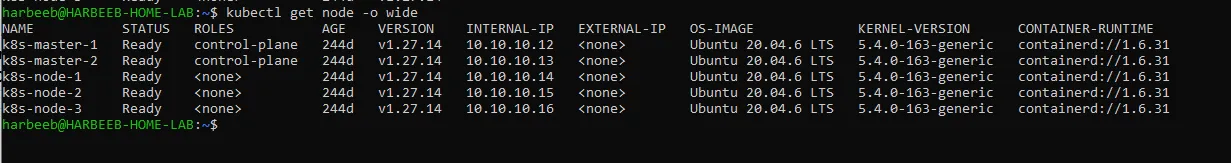
Table of Contents
Introduction
This blog post guides you through building a robust and secure Kubernetes cluster within your home lab environment. We’ll leverage an external etcd cluster for enhanced data management and utilize a Fortigate firewall as a comprehensive network solution.
Fortigate will not only act as a load balancer for the Kubernetes control plane but also serve as a firewall and DHCP server, significantly enhancing the security and manageability of your home lab Kubernetes environment.
By deploying Kubernetes 1.27 on Hyper-V with Fortigate within our home lab, valuable hands-on experience will be gained while building a secure and scalable platform for personal projects or testing purposes.
Prerequisites
- Hyper-V Manager: Installed on your Windows host machine.
- Ubuntu Server 20.04 ISO: Install the operating system on the virtual machines.
- Fortigate CLI or GUI Access: For configuring the firewall.
- Docker: For containerized applications.
- Basic Skills: Hyper-V administration, fundamental Linux commands, and networking fundamentals (IP addressing, subnetting).
- Kubernetes Concepts: Basic understanding of pods, deployments, and services.
Hyper-V Environment Setup
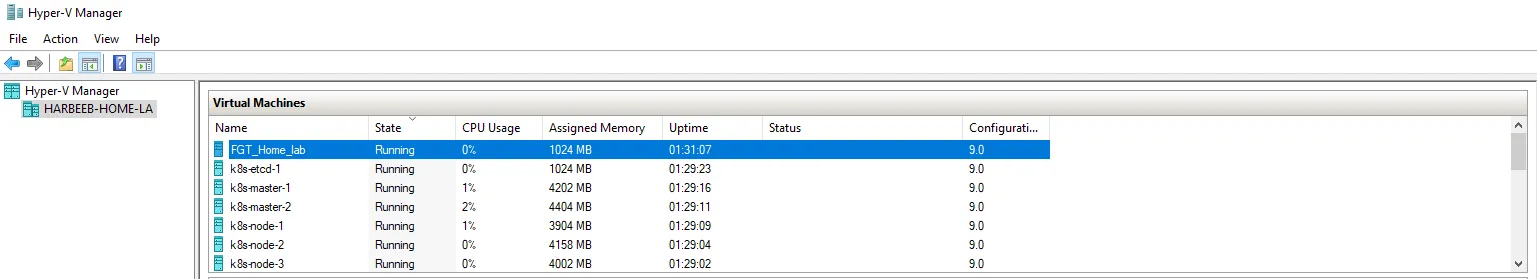
1. Creating Virtual Machines
Create virtual machines for the following roles, allocating appropriate CPU, RAM, and Storage:
- Controller Nodes: Create two virtual machines for high availability.
- Worker Nodes: Create the desired number of worker nodes based on your application needs (3 were used in this scenario).
- etcd Node: Create a dedicated virtual machine for the external etcd cluster.
2. Installing Ubuntu Server 20.04
- Boot each VM from the Ubuntu Server 20.04 ISO.
- During installation, configure networking to use DHCP to obtain an IP address from the FortiGate.
Fortigate Network Configuration
1. DHCP Server Configuration
- Configure the Fortigate internal interface with the DHCP server option to provide dynamic IP addresses to the controller, worker, and other VMs.
- Define appropriate DHCP scopes and options.
2. Firewall Rules
Create firewall rules on Fortigate to:
- Control ingress and egress traffic for applications deployed on the Kubernetes cluster.
- Implement security policies to protect the cluster from external threats.
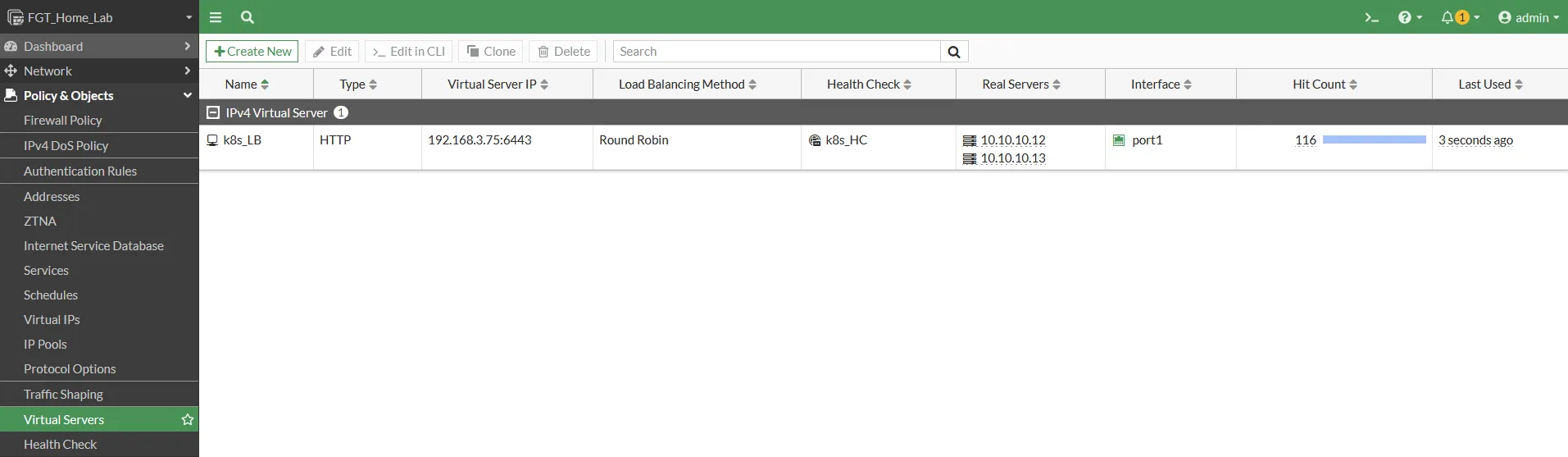
3. Load Balancer Configuration
- Create a Virtual Server on Fortigate to act as the load balancer for the Kubernetes API server.
- Configure health checks to monitor the availability of the controller nodes.
- Define firewall rules to direct traffic to the Virtual Server.
Kubernetes Deployment
1. Setting up the External etcd Cluster
- On the etcd VM, install and configure etcd.
- Ensure proper data persistence by configuring etcd to store data on a reliable storage medium.
- Configure proper certificates for security measures regarding etcd cluster communication with Kubernetes.
2. Installing Kubernetes Control Plane
On each controller node:
- Install Packages: Install the required packages (kubelet, kubeadm, kubectl).
- Initialize Cluster:
- Follow the
kubeadm initcommand to initialize the control plane on the first controller node. - Note: Modify the config file to specify the external etcd node endpoints.
- Follow the
- Join Second Node: Join the second controller node to the cluster using the join command generated by the init process.
- Install kubectl: Download and install the kubectl command-line tool on your local machine or in the cluster.
3. Joining Worker Nodes
- Install required packages (kubelet, kubeadm).
- Configure kubelet on each worker node to point to the API server of the control plane.
- Important: Since two control planes are used, point this to the Fortigate Load Balancer IP address, not the individual node IPs.
- Use the provided join command to add the worker nodes to the cluster.
Testing and Verification
1. Deploy an Application
- Deploy a sample application (e.g., a simple Nginx web server) to the Kubernetes cluster.
- Verify that the application is running correctly and accessible.
2. Verify Cluster Health
- Run
kubectl get nodesand check the health status of all nodes. Verify that all nodes are in the “Ready” state. - Run
kubectl get pods --all-namespacesto check the status of pods running in the cluster. Ensure all pods are in aRunningorSucceededstate.
Conclusion
This blog post demonstrates building a highly secure and scalable Kubernetes cluster on Hyper-V by leveraging Fortigate as a comprehensive network solution. By integrating Fortigate as the DHCP server, firewall, and load balancer, you can significantly enhance the security and manageability of your Kubernetes environment.
This approach provides a deeper understanding of the underlying components and their interactions within a Kubernetes cluster.
References
- Kubernetes Documentation: https://kubernetes.io/
- Fortigate Documentation: https://www.fortinet.com/
- Hyper-V Documentation: Microsoft Learn